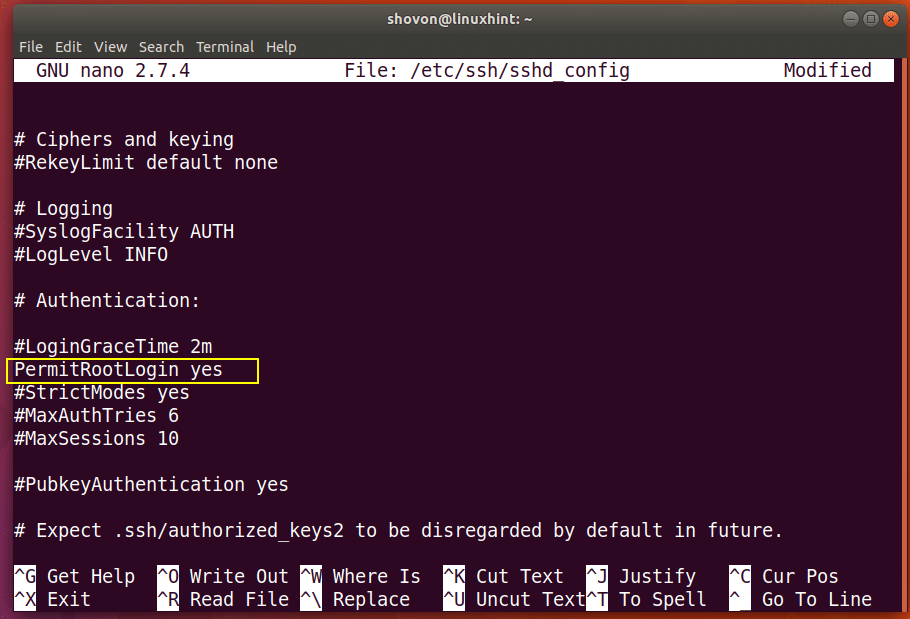
Prerequisites
Jul 31, 2019 Restart SSH Service Command The command to restart sshd are as follows (you must login as root user). You must run command as per your Linux distribution or Unix variant. CentOS / RHEL / Fedora / Redhat Linux Restart SSH.
Sudo stop ssh sudo start ssh As it leverages upstart, this is The Best Way™ to do it, rather than using /etc/init.d/ssh, service, or invoking sshd directly. Make sure to run both commands; if you get an error on stop ssh, start ssh anyway and see what it says—the service could already be stopped. Secure Shell (SSH) is a UNIX-based command interface and protocol for securely getting access to a remote computer. SSH is actually a suite of three utilities - slogin, ssh, and scp - that are secure versions of the earlier UNIX utilities, rlogin, rsh, and rcp. SSH commands are encrypted and secure in several ways. May 23, 2020 How do I start / stop, OR restart the ssh server under Ubuntu Linux operating system using command line options? You need to run a script called /etc/init.d/ssh to stop, start, and restart the OpenSSH server. You can also use the service command to control a System V init script. Ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 2048. This will generate the SSH key. Press Enter at the following prompt to save the key in the default location. You will then be prompted to enter a secure passphrase but you can leave that blank. Add SSH keys to your VM. In the previous step, we generated an SSH key pair.
A ssh server should run on a remote host, since PyCharm runs remote interpreter via ssh-session.
If you want to copy your sources to a remote computer, create a deployment configuration, as described in the section Create a remote server configuration.
Configuring remote Python interpreter via SSH credentials
Create a new a remote Python interpreter via SSH credentials
Ensure that you have downloaded and installed Python on your computer.
Do one of the following:
Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose Add Interpreter.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the project Settings/Preferences and go to Project <project name> | Python Interpreter. Then click the icon and select Add.
In the left-hand pane of the Add Python Interpreter dialog, click SSH Interpreter.
In the right-hand pane select New server configuration, then specify server information (host, port, and username).
In the next dialog window, provide the authentication details to connect to the target server.
Select Password or Key pair (OpenSSL or PuTTY) and enter your password or passphrase. If Key pair (OpenSSL or PuTTY) is selected, specify:
Private key file: location of the file with a private key
Passphrase: similar to a password, it serves to encrypt the private key.
The RFC 4716 format for OpenSSH keys is not supported by PyCharm. See the workaround.
Click Next to proceed with the final configuration step.
In the next dialog window, verify the path to the desired Python interpreter. You can accept default, or specify a different one. You have to configure the path mappings between your local project and the server. To do that, click next to the Sync folders field and enter the path to the local project folder and the path to the folder on the remote server.
You can also select the lowest checkbox to enable automatic upload of the local changes to the remote server.
Select the Execute code using this interpreter with root privileges via sudo checkbox to run an SSH interpreter using sudo. The root privileges will be enabled only for launching the remote interpreter. Files will be copied to the remote server with your current user privileges.
Click Finish to complete adding an interpreter.
Create a new a remote Python interpreter using an SSH configuration
Ensure that you have downloaded and installed Python on your computer.
Do one of the following:
Click the Python Interpreter selector and choose Add Interpreter.
Press Ctrl+Alt+S to open the project Settings/Preferences and go to Project <project name> | Python Interpreter. Then click the icon and select Add.
In the left-hand pane of the Add Python Interpreter dialog, click SSH Interpreter.
In the right-hand pane Existing server configuration and choose any available SSH configuration from the list.
You can also create a new SSH configuration in the SSH Configurations dialog.
Click and fill the required fields. Once done, the newly created SSH configuration will appear in the list of available configurations. It will also become available in the SSH Deployment Configurations settings.
Click Next to continue configuring an interpreter.
In the next dialog window, verify the path to the desired Python interpreter. You can accept default, or specify a different one. You have to configure the path mappings between your local project and the server. To do that, click next to the Sync folders field and enter the path to the local project folder and the path to the folder on the remote server.
You can also select the lowest checkbox to enable automatic upload of the local changes to the remote server.
Select the Execute code using this interpreter with root privileges via sudo checkbox to run an SSH interpreter using sudo. The root privileges will be enabled only for launching the remote interpreter. Files will be copied to the remote server with your current user privileges.
Click Finish to complete adding an interpreter.
In case of adding an interpreter as a root user, you will be asked to provide your password.
Select Remember to keep using the password for this interpreter even you restart PyCharm. The interpreters added with root privileges are marked with sudo in the list of the available interpreters.
How to restart the SSHD service on Windows.
Requirements user or command shell need elevated privileges
Note: Any users connected to the SSH server will be disconnected when the SSH is restarted.
The GSW SSH Server reads configuration values each time the GSW_SSHD service is started. It is the mechanism to read the configuration registry keys into the SSH Server and apply those values.
Two options for re-starting the GSW SSH Service are:
Option 1: In the Windows Start, Search or Run command enter services.msc and press enter
- Select the Extended tab at the bottom
- Select Georgia Softworks GSW_SSHD service
Click Restart the service.
Install eclipse for mac. Figure 1: Restart SSHD Services for Windows
The Georgia SoftWorks GSW_SSHD service and the Georgia SoftWorks Universal Terminal Server should both have a status of Started and a Startup Type of Automatic. Using the Windows Services utility is the recommended method to start and stop the GSW services when required.
| Option 2: | You may use a batch program or windows command shell to restart SSH service. In the Windows Start Menu, search box type in cmd.exe and in the results right click cmd.exe and select Run as administrator. |
In the command shell enter the following.
net stop gsw_sshd && net start gsw_sshd
Figure 2: Command shell to restart the GSW SSHD Service
Confirm that the GSW SSH Service is running.
Using the Installation Status Program Item within Georgia SoftWorks UTS program group, you can view the Installation Status of the GSW UTS and SSH Server.
Restart Ssh Unix
Figure 3: SSH Service Installation Status
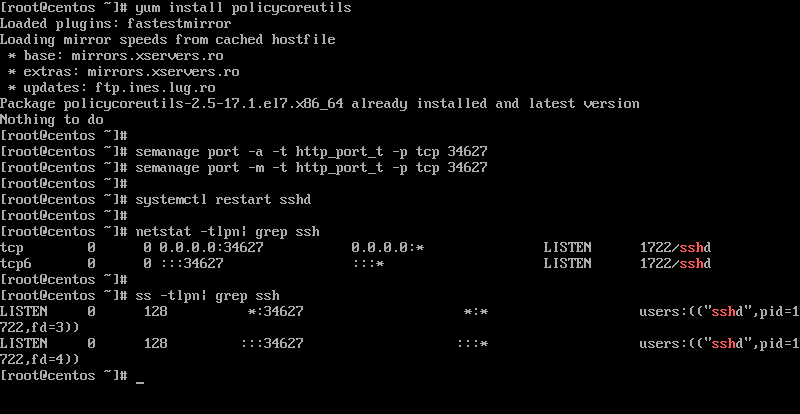
Restart Sshd Centos
View the row “Georgia SoftWorks SSH Shield”. The far right column “running” should have a ✔ check in the check box as shown above.
Ssh Restart Linux
Hon for mac os. Watch How to restart SSH service on Windows
Restart Ssh Server
Back to SSH Server FAQ
Document Number: FAQ-SSH-EX030001081519