This article is a jupyter Notebook beginner guide. Learn what is a jupyter notebook, how to use it and some of the best practices and tips.
- Use this tutorial to learn how to create your first Jupyter Notebook, important terminology, and how easily notebooks can be shared and published online.
- It is an interactive computational environment, in which you can combine code. For more details on the Jupyter Notebook, please see the Jupyter website.
A package that works like the Jupyter Notebook, but inside Atom. It's registered as an opener for .ipynb files — try opening one!
Install
- Install dependencies:
OS X
- Python 3:
brew install python3(there are issues with pip2 and OS X 10.11) - Jupyter and Jupyter Kernel Gateway:
pip3 install jupyter jupyter_kernel_gateway
Linux (Debian)
- Python:
sudo apt-get install python python-pip - Jupyter and Jupyter Kernel Gateway:
pip install jupyter jupyter_kernel_gateway
apm install jupyter-notebookor search for jupyter-notebook inside of Atom
Usage
- Run cell: SHIFT+ENTER, CMD+ENTER (or CTRL+ENTER on Windows)

Developers
Install
git clone https://github.com/jupyter/atom-notebook.gitapm installapm link
Achitecture
This package is built on React and the Flux architecture.
Give Heading In Jupyter Notebook
Map
- main tells Atom how to render
NotebookEditorand registers as an Opener for.ipynbfiles - dispatcher is a singleton flux.Dispatcher which contains the list of valid actions
- notebook-editor is the Store and handles all of the business logic. It loads the file in, creates a state, then receives Actions and updates the state accordingly.
- notebook-editor-view, notebook-cell, text-editor, display-area are the views. notebook-editor-view updates its state by fetching it from notebook-editor, then passes appropriate bits of that state down to the other views as props.
Flow
Rendering:NotebookEditor -> NotebookEditorView -> [child views]

Updating:[external action] -> Dispatcher.dispatch -> NotebookEditor.onAction ?-> NotebookEditor._onChange -> NotebookEditorView._onChange
Immutable state

The state returned by NotebookEditor.getState is an Immutable.js object.
Accessing its properties inside a view looks like this:
Changing it (in NotebookEditor) looks like this:
or this:
Since React requires a view's state to be a regular JS object, the state of NotebookEditorView takes the form:
No other views have state.
To do
- autocomplete
atom.workspace.getActiveTextEditor()returnsundefinedbecauseatom.workspace.getActivePaneItem()returns our custom NotebookEditor class which contains one or more TextEditors, therefore autocomplete, find, and features provided by other packages don't work in cells
- add more actions (duplicate cell, restart kernel, change cell type, etc)
- tell React our rendering is pure
- test rendering performance with big notebooks
- Jupyter Tutorial
- IPython
- Jupyter
- QtConsole
- JupyterLab
Jupyter Notebook Heading
- Jupyter Resources
- Selected Reading
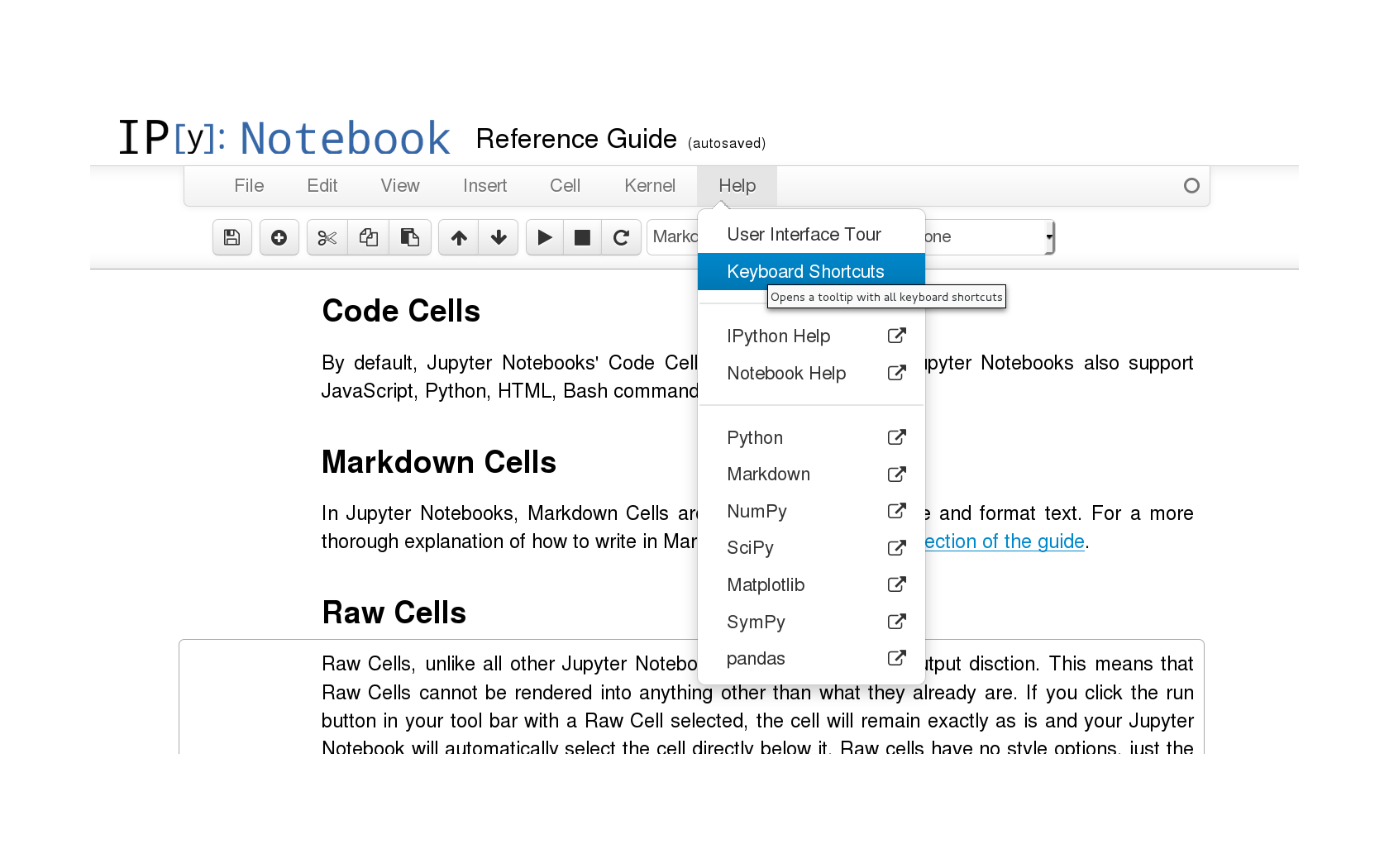
While the menu bar and toolbar lets you perform various operations on notebook, it is desirable to be able to use keyboard shortcuts to perform them quickly.
Jupyter Notebooks have two different keyboard input modes −
Command Mode − Binds the keyboard to notebook level actions. Indicated by a grey cell border with a blue left margin.
Edit Mode − When you are typing in a cell. Indicated by a green cell border.
Writing Heading In Jupyter Notebook
Command Mode (press Esc to enable)
F | find and replace | 1 | change cell to heading 1 |
Ctrl-Shift-F | open the command palette | 2 | change cell to heading 2 |
Ctrl-Shift-P | open the command palette | 3 | change cell to heading 3 |
Enter | enter edit mode | 4 | change cell to heading 4 |
P | open the command palette | 5 | change cell to heading 5 |
Shift-Enter | run cell, select below | 6 | change cell to heading 6 |
Ctrl-Enter | run selected cells | A | insert cell above |
Alt-Enter | run cell and insert below | B | insert cell below |
Y | change cell to code | X | cut selected cells |
M | change cell to markdown | C | copy selected cells |
R | change cell to raw | V | paste cells below |
K | select cell above | Z | undo cell deletion |
Up | select cell above | D,D | delete selected cells |
Down | select cell below | Shift-M | merge selected cells, or current cell with cell below if only one cell is selected |
J | select cell below | Shift-V | paste cells above |
Shift-K | extend selected cells above | L | toggle line numbers |
Shift-Up | extend selected cells above | O | toggle output of selected cells |
Shift-Down | extend selected cells below | Shift-O | toggle output scrolling of selected cells |
Shift-J | extend selected cells below | I,I | interrupt the kernel |
Ctrl-S | Save and Checkpoint | 0,0 | restart the kernel (with dialog) |
S | Save and Checkpoint | Esc | close the pager |
Shift-L | toggles line numbers in all cells, and persist the setting | Q | close the pager |
Shift-Space | scroll notebook up | Space | scroll notebook down |
Edit Mode (press Enter to enable)
Tab | code completion or indent | Ctrl-Home | go to cell start |
Shift-Tab | tooltip | Ctrl-Up | go to cell start |
Ctrl-] | indent | Ctrl-End | go to cell end |
Ctrl-[ | dedent | Ctrl-Down | go to cell end |
Ctrl-A | select all | Ctrl-Left | go one word left |
Ctrl-Z | undo | Ctrl-Right | go one word right |
Ctrl-/ | comment | Ctrl-M | enter command mode |
Ctrl-D | delete whole line | Ctrl-Shift-F | open the command palette |
Ctrl-U | undo selection | Ctrl-Shift-P | open the command palette |
Insert | toggle overwrite flag | Esc | enter command mode |
Ctrl-Backspace | delete word before | Ctrl-Y | redo |
Ctrl-Delete | delete word after | Alt-U | redo selection |
Shift-Enter | run cell, select below | Ctrl-Shift-Minus | split cell at cursor |
Ctrl-Enter | run selected cells | Down | move cursor down |
Alt-Enter | run cell and insert below | Up | move cursor up |
Ctrl-S | Save and Checkpoint |
